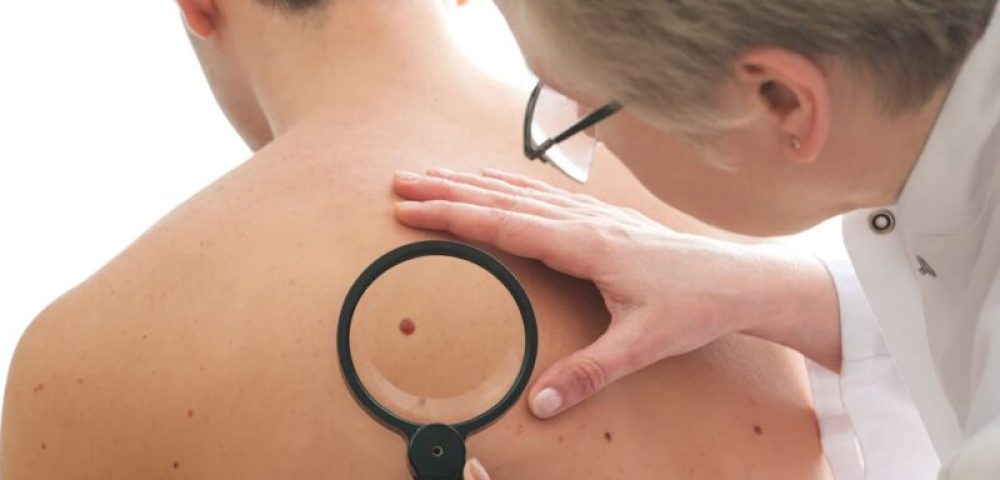
Skin cancer, in its essence, is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal skin cells. It arises when DNA damage to skin cells (most often caused by ultraviolet radiation from sunshine or tanning beds) triggers mutations, or genetic defects, that lead the skin cells to multiply rapidly and form malignant tumors.
The most common types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma, each presenting unique challenges and requiring distinct approaches to treatment.
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, collectively known as non-melanoma skin cancers, are the more prevalent forms and are generally less aggressive. Melanoma, on the other hand, is less common but far more dangerous if not caught early, due to its propensity to spread to other parts of the body.
The Sun’s Role: A Double-Edged Sword

The sun, vital for life, plays a paradoxical role in the tale of skin cancer. Its ultraviolet (UV) rays are the primary cause of skin damage that can lead to cancer. UV radiation comes in three types – UVA, UVB, and UVC, with UVA and UVB being the main culprits behind skin cancer.
UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin and are primarily responsible for aging effects, while UVB rays cause more superficial skin damage, leading to sunburn. Both contribute to the risk of skin cancer.
Prevention: The First Line of Defense
Preventing skin cancer hinges on protecting the skin from excessive sun exposure and harmful UV rays. This entails seeking shade during peak sun hours (usually between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.), wearing protective clothing such as long-sleeved shirts, pants, and broad-brimmed hats, and applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF. Sunscreen should be reapplied every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
Moreover, awareness of the dangers of tanning beds is crucial. The concentrated UV radiation from tanning beds significantly increases the risk of skin cancer, and avoiding them can markedly reduce one’s risk.
Early Detection: The Key to Survival
Early detection of skin cancer greatly increases the chances of successful treatment and survival, particularly with melanoma. Regular skin examinations, both self-exams and professional exams by a dermatologist, are paramount.
Individuals should be vigilant about new moles or changes to existing moles, adhering to the ABCDE rule as a guideline: Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color that is not uniform, Diameter greater than 6 mm, and Evolving size, shape or color.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
The landscape of skin cancer detection and treatment is continually evolving, with advances in technology playing a pivotal role. Digital dermatoscopy, for instance, allows dermatologists to examine moles more thoroughly, while AI-driven tools are being developed to help identify skin cancer early. These technologies, coupled with traditional methods, enhance the ability to detect skin cancer at its nascent stages.
Lifestyle and Skin Cancer Risk

Lifestyle factors also play a significant role in skin cancer risk. Diet, exercise, and avoiding smoking can all contribute to lower cancer risk in general. Nutrients such as vitamins A, C, E, and selenium have been linked to skin health, potentially offering protective benefits against UV damage.
| Type of Skin Cancer | Characteristics | Common Locations | Treatment Options |
| Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) | Slow-growing; appears as a translucent, pearly bump | Face, ears, neck, scalp, shoulders | Surgical removal, topical treatments, radiation therapy |
| Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) | May appear as a firm, red nodule or a flat lesion with a scaly crust | Face, ears, neck, hands, arms | Surgical removal, radiation therapy, cryotherapy |
| Melanoma | Malignant; can develop in existing moles or appear suddenly as a new dark spot | Anywhere on the body, including areas not exposed to the sun | Surgical removal, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, chemotherapy |
Community and Awareness
Raising awareness about skin cancer prevention and the importance of early detection is crucial. Community programs, educational campaigns, and social media can play significant roles in disseminating information and encouraging proactive health behaviors. Schools, workplaces, and health organizations can collaborate to provide resources and screenings, fostering a culture of prevention and health literacy.
The Path Forward
The rising tide of skin cancer presents a formidable challenge, yet it is one that can be met with informed action and collective resolve. Prevention, through protective measures against UV exposure, and early detection, through regular skin checks, stand as pillars in the fight against skin cancer. Advances in technology and a commitment to lifestyle choices that support overall health further reinforce these efforts.
FAQs

Can diet really affect my risk of developing skin cancer?
Yes, diet can influence your risk of developing skin cancer. Consuming a diet rich in antioxidants, found in fruits and vegetables, can help protect your skin cells from UV damage.
Foods high in beta-carotene, vitamins C and E, and other antioxidants have been shown to contribute to skin health. However, it’s important to remember that diet is just one aspect of prevention and should be combined with other protective measures against UV exposure.
How often should I see a dermatologist for a skin examination?
The frequency of dermatologist visits for a skin examination varies depending on your risk factors for skin cancer. Individuals with a higher risk (those with a family history of skin cancer, a history of excessive sun exposure, or numerous moles on their skin) may need yearly exams.
Those at lower risk might require less frequent checks. It’s best to consult with a dermatologist to determine the most appropriate schedule for you.
Are there any specific types of clothing that offer better protection against the sun?
Yes, clothing that offers better protection against the sun typically has a tight weave or knit and is made of unbleached cotton, high-luster polyesters, and satin-finished fabrics.
These materials reflect more UV radiation than others. Additionally, specially designed sun-protective clothing with an Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) rating provides significant protection by absorbing or blocking harmful UV rays.
Is it possible to get skin cancer in areas of the skin not exposed to the sun?
Yes, it is possible to develop skin cancer in areas not typically exposed to the sun. While UV radiation is a major risk factor for skin cancer, other factors such as genetics and exposure to certain chemicals can also contribute to the development of skin cancer in areas like the palms, soles, under nails, and within mucous membranes.
Can makeup offer any protection against UV rays?
Some makeup products contain SPF (Sun Protection Factor) and can offer additional protection against UV rays. However, makeup should not be relied upon as the sole form of sun protection. It’s important to use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher under makeup. Remember to reapply sunscreen every two hours, as makeup does not provide long-lasting protection.
What steps can I take to reduce my child’s risk of skin cancer?
Protecting your child’s skin from an early age is crucial to reduce their long-term risk of skin cancer. Encourage wearing hats and protective clothing, apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30, and limit sun exposure during peak hours.
Instilling these habits early on can help your child maintain healthy skin protection practices throughout their life. Additionally, teaching children about the importance of seeking shade and understanding the dangers of tanning beds is fundamental.
Final Words
As individuals and communities, there is a shared responsibility to face the threat of skin cancer head-on. By fostering awareness, prioritizing prevention, and advocating for early detection, the trajectory of skin cancer can be altered, saving lives and preserving health.
There is an online platform for those needing support when faced with skin cancer disease: Doctor.Global aims to help search for a clinic.
In the battle against skin cancer, knowledge, vigilance, and action are our most powerful weapons. Together, we can stem the rising tide of skin cancer, turning the tide toward a future marked by greater health, awareness, and resilience.
Related Posts: